3D Wireframe Modeling
Every design starts with a wireframe, forming the basis for creative projects using modern technology and software. These wireframes function like blueprints, offering precise measurements and a clear idea of how the final design will appear.
In this discussion, we’ll look at 3D wireframe modeling. We’ll cover how the process works, the benefits it has gained over time, and its limitations.
What Is Wireframe Modeling
Wireframe modeling is a technique that uses 3D computer graphics to represent any three-dimensional object visually. This method combines lines and curves to form the desired 3D wireframe structure. A wireframe model is essentially the blueprint or skeletal framework of an object being developed into a real-world product. Forming lines, points, arcs, curves, circles, and other geometric shapes, these models are constructed with precise dimensions that define the object’s size, edges, and depth. Because an object’s entire concept and design rely on these 3D wireframes, they play an essential role across numerous industries that use 3D modeling techniques. Next, let’s examine the advantages of wireframe modeling, which explains why this method has become indispensable in many industries.
Advantages of 3D wireframe modeling
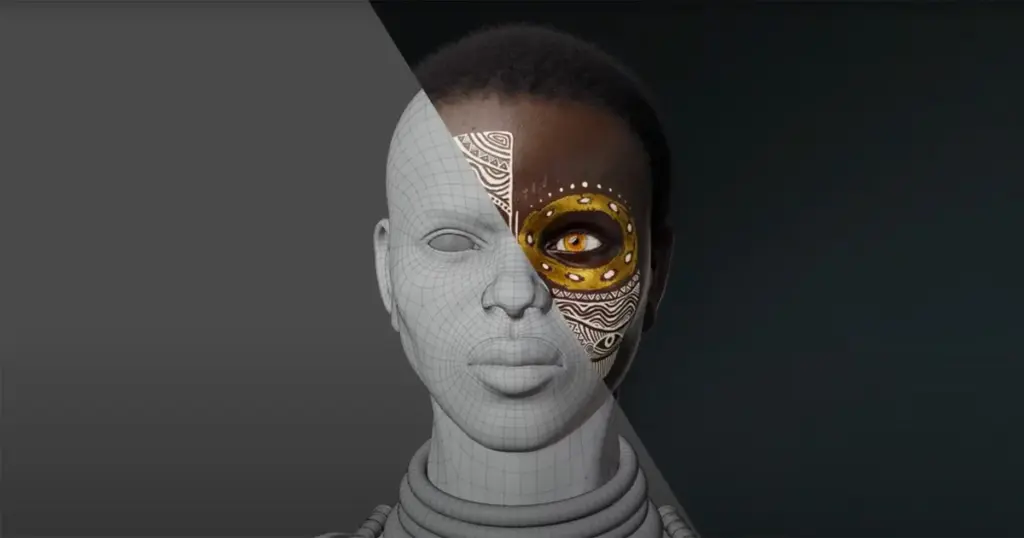

Here are some advantages of 3d wireframe modeling and crucial for the present world.
Provides a 3D View
3d wireframe modeling is important because it gives a complete view of 3d modeling from different forms and angles. This will help to figure out how well the product dimension is. Wireframe modeling offers several advantages, particularly in fields like 3D modeling, CAD design, and engineering. Here are some key benefits:
Simplicity
Wireframe models are simple, using lines and vertices to represent the structure of an object. This simplicity allows for faster creation and manipulation of models.
Clarity in Design
Since wireframes focus on the edges and contours of an object, they provide a clear view of the overall geometry, making it easier to spot inconsistencies or design issues early in the process.
Low System Resource Usage
Wireframe models are lightweight compared to full 3D models with textures and details. This allows for smooth rendering and interaction, even on systems with limited processing power.
Easier Prototyping
Designers can quickly prototype complex shapes without focusing on the final appearance, enabling rapid iteration and testing of ideas.
View Internal Structures
Wireframe models allow you to see through objects, which is helpful when examining internal components or checking for proper fit within an assembly.
Efficient for Drafting and Initial Designs
Before moving to detailed modeling or adding materials, wireframe models help with the basic layout and initial presentation of the design.
Cross-Software Compatibility
Many CAD and 3D modeling programs can export or import wireframes, making them widely compatible across different platforms.
Wireframe modeling is particularly advantageous for quick previews, technical designs, and scenarios where performance and speed are critical.
Limitations
3D wireframe modeling has some limitations that designers need to deal with. One of the challenges is representing an object’s inside and outside surfaces. While 3D models can be quite complicated, wireframe modeling simplifies things, making it easier to spot flaws. It also enhances understanding by allowing designers to view the object from a single dimension, though this may limit the full representation of the object’s surfaces.
- Creating basic and simple designs for faster evaluation and quicker design changes.
- Viewing the model from different angles
- Helps in assessing the design more effectively.
- Analyzing spatial relationships, such as the distance between edges and corners, to spot any potential conflicts.
- Generating improved perspective views (though this feature is not available in AutoCAD LT).
- Creating standard auxiliary and orthographic views with the help of advanced computer systems.
Methods for Creating 3D Wireframe Models
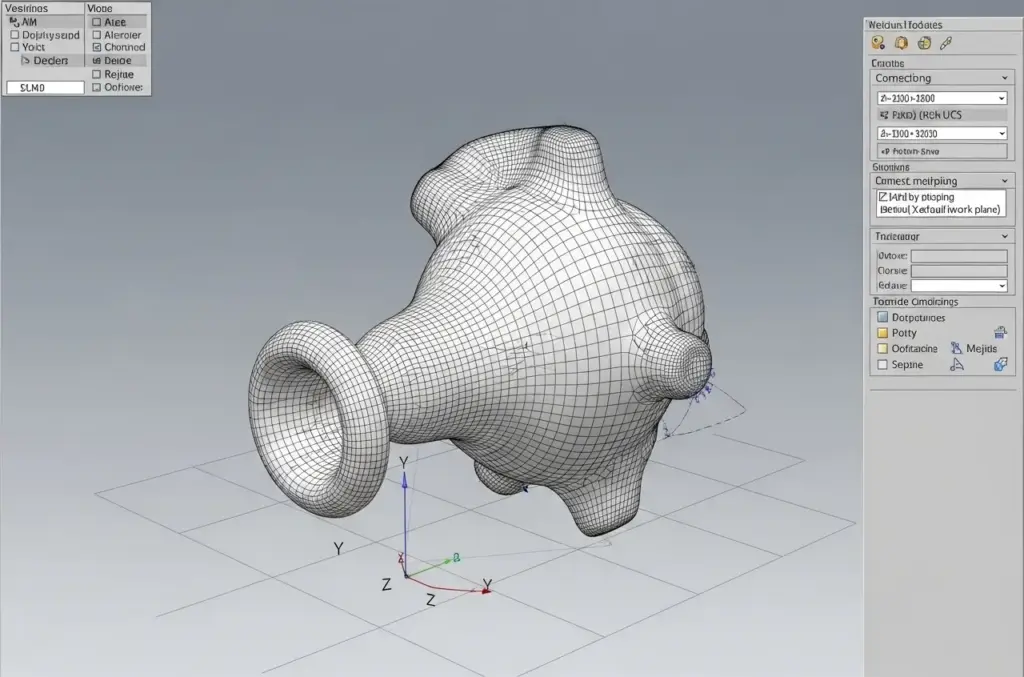
Wireframe modeling requires significant experience and practice, so it’s best to begin with simple steps before attempting complex designs. To create a wireframe model, start by connecting a 2D object in 3D space. Enter the X, Y, and Z coordinates to define key points. Make sure your workspace is set to the default work plane, aligning the X and Y axes of the UCS. From there, you can move, copy, or rotate the object to adjust its position and orientation.
Tips to Create Real-time 3D Wireframe Models
- Minimize visual complexity by deactivating unnecessary layers.
- Utilize isometric views for easier object selection and navigation.
- Apply distinct colors to differentiate various dimensions and views within the model.
- Ensure precise construction geometry to clearly outline the object structure.
- Explore the manipulation of UCS (User Coordinate System) for better control in 3D space.
- Choose the correct images and screenshots to achieve perfect geometric symmetry.
- Use coordinate filters to accurately locate points and create perpendiculars.
Conclusion
3D wireframe modeling offers a foundational approach to 3D design, but it requires patience and practice to master different software such as 3DS max, Maya, etc. Starting with simple models allows designers to build a solid understanding of the process before moving on to more complex structures. Accurate input of X, Y, and Z coordinates ensures that the key points of the model are well-defined. Setting the workspace to the default work plane and using the UCS to align the X and Y axes provides a structured framework for further manipulations, such as moving, copying, or rotating the object.
With time, designers can fully cover the potential of 3D wireframe modeling to visualize and adjust their designs from any angle. This approach allows for easier identification of errors or conflicts and helps improve the overall design flow. As a result, 3D modeling becomes a powerful tool for creating precise, accurate representations, serving as a crucial step in the design and engineering process.